


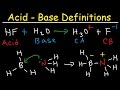














The conjugate base is therefore [Al(H2O)5(OH)]^2+ [1] F. A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, C. A. Murillo, M. Bochmann, Advanced Inorganic Chemistry 6th ed (1999). p 183. 1 0. Still have questions? Get your answers by asking now. Ask Question + 100. Join Yahoo Answers and get 100 points today. Join . Trending Questions. Trending Questions. is it true that The smallest particle of sugar that is still TABLE OF CONJUGATE ACID-BASE PAIRS Acid Base K a (25 oC) HClO 4 ClO 4 – H 2 SO 4 HSO 4 – HCl Cl– HNO 3 NO 3 – H 3 O + H 2 O H 2 CrO 4 HCrO 4 – 1.8 x 10–1 H 2 C 2 O 4 (oxalic acid) HC 2 O 4 – 5.90 x 10–2 [H 2 SO 3] = SO 2 (aq) + H 2 O HSO 3 – 1.71 x 10–2 HSO 4 – SO 4 2– 1.20 x 10–2 H 3 PO 4 H 2 PO 4 – 7.52 x 10–3 Fe(H 2 O) 6 3+ Fe(H 2 O) 5 OH 2+ 1.84 x 10–3 H 2 C Start studying Chapter 6: Acid-Base and Donor-Acceptor Chemistry. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Search. Browse. Create. Log in Sign up. Log in Sign up. Upgrade to remove ads. Only $2.99/month. Chapter 6: Acid-Base and Donor-Acceptor Chemistry. STUDY. Flashcards. Learn. Write. Spell. Test. PLAY. Match. Gravity. Created by. mapatofuu. Key The conjugate base will have one less H atom than the acid H2As04-. So the conjugate base will be HAs042-. There is another negative charge because a proton (aka positive charge aka H atom) is removed. 0 0. Still have questions? Get your answers by asking now. Ask Question + 100. Join Yahoo Answers and get 100 points today. Join. Trending Questions. Trending Questions. What would water be like Copper (I) Oxide – Cu 2 O; BISCO Bismuth Strontium Calcium Copper Oxide – BSCCO; HgO-Mercury(II) oxide; Hexatantalate [Ta 6 O 19] 2-f-block Elements. Lanthanum(III) chloride – LaCl 3; Cerium Tetrafluoride – CeF 4; Gadolinium Orthoferrite – GdFeO 3; Garnet – Ca 3 Al 2 Si 3 O 12 – Grossular; Uranium (V) Chloride – U 2 Cl 10; Solid acid base salt pH ~7 (NH3 (aq)) HCl + NH4OH NH4Cl + H2O strong weak acidic acid base salt pH <7 3HC2H3O2 + Fe(OH)3 Fe(C2H3O2)3 + 3H2O weak weak neutral acid base salt pH ~7 H2CO3 + 2KOH K2CO3 + 2H2O weak strong basic acid base salt pH >7 Strongest acid in water: hydronium ion Strongest base in water: hydroxide ion ALL OF CHAPTER NINE HAS BEEN COMPLETED!!! NOW DO WORKSHEET 4.2 FOR HOMEWORK . Wk Addition of NH3 to Cu2+ resulting in a copper hydroxide ppt. [Cu(H2O)4]2+ + 2 OH- [Cu (H2O)2(OH)2] + 2 H2O Aquo Complex Ion Reactions [Cu(H2O)4]2+ [Cu(NH3)4]2+ Colored transition metal complex ions alter color upon bonding to a different Lewis base. Complex Ions will Complex ions are the chemical basis for colorful paint pigments. Conjugate acids and conjugate bases are the acids and bases that lose or gain protons. NH4+ is the conjugate acid to the base NH3, because NH3 gained a hydrogen ion to form NH4+.The conjugate base of an acid is formed when the acid donates a proton. Correct the misprint and label the acid-conjugate base pair and the Base conjugate acid pair. Given that HSO41- is a stronger acid than HPO41- write the chemical reaction if the solution containing both of these ions are mixed together. (Hint one of these must act as an acid and the other as a base) Reference: Jespersen Section 15.2 This is illustrated below for acetic acid and its conjugate base, the acetate anion. Acetic acid is a weak acid (K a = 1.8 x 10-5) and acetate is a weak base (\(K_{b} = \frac{K_{w}}{K_{a}} = 5.6 \times 10^{10}\)) The strength of a conjugate acid/base varies inversely with the strength or weakness of its parent acid or base. Any acid or base is
[index] [1050] [1792] [9644] [5538] [8905] [6240] [995] [8067] [4267] [906]
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. To see all my Chemistry videos, check outhttp://socratic.org/chemistryHere's how to write formulas for ionic compounds that contain polyatomic ions. In order... This chemistry video tutorial shows you how to identify an ionic compound as acidic, basic, or a neutral salt. You need to know the 6 common strong acids su... Many practice problems for how to calculate and determine oxidation numbers, often referred to as oxidation states. To figure out oxidation numbers for eleme... To tell if NH4Cl (Ammonium chloride) forms an acidic, basic (alkaline), or neutral solution we can use these three simple rules along with the neutralization... This chemistry video tutorial explains the concept of acids and bases using the arrhenius definition, bronsted - lowry and lewis acid base definition. It al... This is an introduction to oxidation reduction reactions, which are often called redox reactions for short. An oxidation reduction (redox) reaction happens w... Need help with Chemistry? Whether you're in high school, college, AP or IB courses, these videos can help! They are also targeted to students studying for the AP Test, SAT, MCAT, DAT, and OAT ... A step-by-step explanation of how to draw the HNO3 Lewis Structure (Nitric Acid). The HNO3 Lewis structure is best thought of as the NO3 with an H attache... A step-by-step explanation of how to draw the CO3 2- Lewis Dot Structure (Carbonate ion).For the CO3 2- structure use the periodic table to find the total nu...
Copyright © 2024 hot.bestrealmoneygame.xyz